Abstract
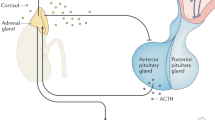
Based on concepts proposed by Langley, Cannon, and Selye, adrenal responses to stress occur in a syndrome that reflects activation of the sympathoadrenal system and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical (HPA) axis; and a “stress syndrome” maintains homeostasis in emergencies such as “fight or flight” situations, but if the stress response is excessive or prolonged then any of a variety of clinical disorders can arise. The idea of a unitary sympathoadrenal system does not account for evidence that different stressors elicit different patterns of autonomic responses, with exposure to some stressors differentially affecting sympathetic noradrenergic and adrenomedullary hormonal activities. Instead, adrenomedullary responses to stressors are more closely tied to adrenocortical than to sympathetic noradrenergic responses. Distress involves concurrent activation of the HPA and adrenomedullary neuroendocrine systems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breier A, Davis O, Buchanan R et al (1992) Effects of alprazolam on pituitary-adrenal and catecholaminergic responses to metabolic stress in humans. Biol Psychiatry 32:880–890
Cannon WB (1929a) Organization for physiological homeostasis. Physiol Rev 9:399–431
Cannon WB (1929b) Bodily changes in pain, hunger, fear and rage. D. Appleton & Co., New York
Cannon WB (1931) The effects of progressive sympathectomy on blood pressure. Am J Physiol 97:592–595
Cannon WB (1939) The wisdom of the body. W.W. Norton, New York
Cannon WB, Lissak K (1939) Evidence for adrenaline in adrenergic neurones. Am J Physiol 125:765–777
Chrousos GP, Gold PW (1992) The concepts of stress and stress system disorders. Overview of physical and behavioral homeostasis. J Am Med Assoc 267:1244–1252
Cryer PE (1980) Physiology and pathophysiology of the human sympathoadrenal neuroendocrine system. N Engl J Med 303:436–444
Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Bornstein SR (2008) Cross-talk between adrenal medulla and adrenal cortex in stress. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1148:112–117
Frank SM, Cattaneo CG, Wieneke-Brady MB et al (2002) Threshold for adrenomedullary activation and increased cardiac work during mild core hypothermia. Clin Sci 102:119–125
Fukuhara K, Kvetnansky R, Cizza G et al (1996) Interrelations between sympathoadrenal system and hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical/thyroid systems in rats exposed to cold stress. J Neuroendocrinol 8:533–541
Gauthier P, Nadeau R, De Champlain J (1972) Acute and chronic cardiovascular effects of 6-hydroxydopamine in dogs. Circ Res 31:207–217
Gerra G, Zaimovic A, Mascetti GG et al (2001) Neuroendocrine responses to experimentally-induced psychological stress in healthy humans. Psychoneuroendocrinology 26:91–107
Goldstein DS (1995a) Stress as a scientific idea: a homeostatic theory of stress and distress. Homeostasis 4:177–215
Goldstein DS (1995b) Stress, catecholamines, and cardiovascular disease. Oxford University Press, New York
Goldstein DS (2001) The autonomic nervous system in health and disease. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY
Goldstein DS (2006) Adrenaline and the inner world: an introduction to scientific integrative medicine. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, MD
Goldstein DS, Frank SM (2001) The wisdom of the body revisited: the adrenomedullary response to mild core hypothermia in humans. Endocr Regul 35:3–7
Goldstein DS, Kopin IJ (2008) Adrenomedullary, adrenocortical, and sympathoneural responses to stressors: a meta-analysis. Endocr Regul 42:111–119
Goldstein DS, McEwen B (2002) Allostasis, homeostats, and the nature of stress. Stress 5:55–58
Goldstein DS, Garty M, Bagdy G et al (1993) Role of CRH in glucopenia-induced adrenomedullary activation in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 5:475–486
Julien C, Kandza P, Barres C, Lo M, Cerutti C, Sassard J (1990) Effects of sympathectomy on blood pressure and its variability in conscious rats. Am J Physiol 259:H1337–H1342
Juster RP, McEwen BS, Lupien SJ (2010) Allostatic load biomarkers of chronic stress and impact on health and cognition. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:2–16
Kvetnansky R, Pacak K, Fukuhara K et al (1995) Sympathoadrenal system in stress. Interaction with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system. Ann N Y Acad Sci 771:131–158
Lake CR, Ziegler MG, Kopin IJ (1976) Use of plasma norepinephrine for evaluation of sympathetic neuronal function in man. Life Sci 18:1315–1325
Mansour VM, Wilkinson DJ, Jennings GL, Schwarz RG, Thompson JM, Esler MD (1998) Panic disorder: coronary spasm as a basis for cardiac risk? Med J Aust 168:390–392
McEwen BS (1998) Stress, adaptation, and disease. Allostasis and allostatic load. Ann N Y Acad Sci 840:33–44
McEwen BS (2000) Allostasis and allostatic load: implications for neuropsychopharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:108–124
McEwen B, Stellar E (1993) Stress and the individual. Mechanisms leading to disease. Arch Intern Med 153:2093–2101
Pacak K, Palkovits M, Yadid G, Kvetnansky R, Kopin IJ, Goldstein DS (1998) Heterogeneous neurochemical responses to different stressors: a test of Selye’s doctrine of nonspecificity. Am J Physiol 275:R1247–R1255
Patel JN, Coppack SW, Goldstein DS, Miles JM, Eisenhofer G (2002) Norepinephrine spillover from human adipose tissue before and after a 72-hour fast. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3373–3377
Robertson DA, Johnson GA, Robertson RM, Nies AS, Shand DG, Oates JA (1979) Comparative assessment of stimuli that release neuronal and adrenomedullary catecholamines in man. Circulation 59:637–643
Schachter S, Singer J (1962) Cognitive, social, and physiological determinants of emotional state. Psychol Rev 69:379–399
Schulkin J, Gold PW, McEwen BS (1998) Induction of corticotropin-releasing hormone gene expression by glucocorticoids: implication for understanding the states of fear and anxiety and allostatic load. Psychoneuroendocrinology 23:219–243
Selye H (1974) Stress without Distress. New American Library, New York
Shah SD, Tse TF, Clutter WE, Cryer PE (1984) The human sympathochromaffin system. Am J Physiol 247:E380–E384
Sharabi Y, Dendi R, Holmes C, Goldstein DS (2003) Baroreflex failure as a late sequela of neck irradiation. Hypertension 42:110–116
Siegel S (1972) Conditioning of insulin effects. J Comp Physiol Psychol 78:233–241
Sofuoglu M, Nelson D, Babb DA, Hatsukami DK (2001) Intravenous cocaine increases plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine in humans. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 68:455–459
Somerfield MR, McCrae RR (2000) Stress and coping research. Methodological challenges, theoretical advances, and clinical applications. Am Psychol 55:620–625
Staten MA, Matthews DE, Cryer PE, Bier DM (1987) Physiological increments in epinephrine stimulate metabolic rate in humans. Am J Physiol 253:E322–E330
Udelsman R, Goldstein DS, Loriaux DL, Chrousos GP (1987) Catecholamine-glucocorticoid interactions during surgical stress. J Surg Res 43:539–545
Wilkinson DJC, Thompson JM, Lambert GW et al (1998) Sympathetic activity in patients with panic disorder at rest, under laboratory mental stress, and during panic attacks. Arch Gen Psychiatry 55:511–520
Yoshida-Hiroi M, Bradbury MJ, Eisenhofer G et al (2002) Chromaffin cell function and structure is impaired in corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor type 1-null mice. Mol Psychiatry 7:967–974
Young JB, Landsberg L (1979) Sympathoadrenal activity in fasting pregnant rats: dissociation of adrenal medullary and sympathetic nervous system responses. J Clin Invest 64:109–116
Young JB, Rosa RM, Landsberg L (1984) Dissociation of sympathetic nervous system and adrenal medullary responses. Am J Physiol 247:E35–E40
Zuckerman-Levin N, Tiosano D, Eisenhofer G, Bornstein S, Hochberg Z (2001) The importance of adrenocortical glucocorticoids for adrenomedullary and physiological response to stress: a study in isolated glucocorticoid deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:5920–5924
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A commentary to this article can be found at doi:10.1007/s10571-010-9607-8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goldstein, D.S. Adrenal Responses to Stress. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30, 1433–1440 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9606-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-010-9606-9